Vagus Nerve Training: The Secret to Boosting Your Emotional and Physical Resilience

Stress is an inevitable part of our lives, and managing it effectively is crucial for our mental and physical well-being. One of the key players in stress regulation is the vagus nerve, a complex network of nerves that runs from the brainstem to the abdomen.
In this article, we will explore the importance of vagus nerve training for stress management and overall well-being.

So What Does Training the Vagus Nerve Actually Do?
When we train our vagus nerve, we are essentially training our nervous system to shift into a state of calm and relaxation. This is achieved by stimulating the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating our bodily functions at rest. By activating the vagus nerve, we can improve our heart rate variability, which is an indicator of our body's ability to adapt to stress.
During vagus nerve training, we may experience shifts in our brainwave states, with an increase in alpha and theta waves associated with relaxation and meditation. This can help us achieve a state of calm and improve our mental clarity and focus. Additionally, vagus nerve stimulation can activate the release of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which can promote feelings of happiness and well-being.
Lets break this down a little further...
"I can say things like parasympathetic nervous system, brainwave states and heart rate variability but if you don't understand it, well it just won't make sense, so lets dive in with more clarity below"
The parasympathetic nervous system is one of the two main branches of the autonomic nervous system, which controls our involuntary bodily functions like heart rate, breathing, and digestion. The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for our "rest and digest" response, where it slows down our heart rate, relaxes our muscles, and improves digestion.
One way to measure the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system is through heart rate variability (HRV). HRV is the variation in time between each heartbeat and is an indicator of how well our body can adapt to stressors.
A high HRV means that our body can easily switch between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, allowing us to respond to stress effectively and then return to a state of relaxation.
Training the vagus nerve can help improve HRV by strengthening the parasympathetic nervous system. This can be achieved by using techniques like deep breathing, meditation, yoga, and cold exposure to shift the body into a state of relaxation, which triggers the parasympathetic response.
Brainwave states refer to the different frequencies of electrical activity in the brain. There are five main types of brainwave states: Gamma, Beta, Alpha, Theta, and Delta.

-
Gamma Waves: These are the fastest brainwaves, ranging from 30 to 100 Hz. They are associated with higher states of consciousness, such as intense focus, deep meditation, and peak performance.
-
Beta Waves: These are the most common brainwaves and range from 12 to 30 Hz. They are associated with normal waking consciousness, including alertness, concentration, and logical thinking.
-
Alpha Waves: These brainwaves range from 8 to 12 Hz and are associated with relaxed, calm, and creative states of consciousness, such as daydreaming, visualisation, and light meditation.
-
Theta Waves: These brainwaves range from 4 to 8 Hz and are associated with deeper states of relaxation, meditation, and hypnosis. They are also associated with creativity, intuition, and spiritual experiences.
-
Delta Waves: These are the slowest brainwaves, ranging from 0.5 to 4 Hz. They are associated with deep sleep, physical healing, and rejuvenation.
Each of these brainwave states plays a unique role in our overall mental and physical health, and understanding them can help us optimise our brain function and well-being.
By practicing techniques like meditation, we can shift our brainwave state from gamma to beta to alpha, and even into theta. This helps to activate the parasympathetic nervous system.
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that are released by neurones in the brain and transmit messages between them. Serotonin and dopamine are two of the most well-known neurotransmitters. Serotonin is often referred to as the "feel-good" chemical because it helps regulate mood, appetite, and sleep. Dopamine is often associated with pleasure and reward, as it is released when we experience something pleasurable or rewarding.
When we train our vagus nerve and activate the parasympathetic nervous system, this can lead to an increase in the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. This can result in an overall improvement in our mood and sense of well-being. Additionally, an increase in HRV has been associated with a reduction in stress-related disorders, such as anxiety and depression.
Overall, by training the vagus nerve and activating the parasympathetic nervous system, we can improve HRV, shift brainwave states, and increase the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. This can lead to a sense of calm and well-being, improved mood, and a reduction in stress-related disorders.
What is the Vagus Nerve?
The vagus nerve is the longest and most complex of the cranial nerves in the body. It plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions, including heart rate, digestion, and respiration. The vagus nerve is also involved in the stress response, helping the body to calm down after a stressful event.

What are Cranial Nerves?
A cranial nerve is like a special pathway in your body that helps your brain communicate with other parts of your body. Just like how your phone needs Wi-Fi or internet connection to communicate with other devices, your brain needs these special pathways to tell your body what to do. There are twelve cranial nerves in total and each one helps with different things, like seeing, hearing, smelling, and even tasting yummy food.
The Importance of Training the Vagus Nerve
Training the vagus nerve can have significant benefits for our stress levels, emotional regulation, and performance.
Studies have shown that activating the vagus nerve can stimulate the relaxation response, reducing stress levels and promoting a sense of calmness and well-being.
5 Benefits of Calmness and Wellbeing
-
Reduced stress: When we feel calm and centred, our stress levels decrease. This can help us to feel more relaxed and able to handle challenging situations without becoming overwhelmed.
-
Improved focus: When our minds are calm, it is easier to concentrate on the task at hand. We are better able to pay attention and be present in the moment, which can help us to be more productive and effective in our work and personal lives.
-
Better physical health: Chronic stress can have negative effects on our physical health, such as increased blood pressure and a weakened immune system. By reducing stress through calmness and wellbeing practices, we can improve our overall physical health and reduce the risk of chronic illnesses.
-
Improved relationships: When we are calm and centered, we are better able to communicate effectively and empathetically with others. This can lead to stronger and more positive relationships with friends, family, and coworkers.
-
Greater happiness and life satisfaction: Calmness and wellbeing practices can help us to cultivate a greater sense of inner peace and contentment. By prioritising our own wellbeing and taking time to care for ourselves, we can experience greater happiness and fulfillment in our lives.
On the other hand, not improving vagus nerve function can have negative effects on our physical and mental health. Poor vagus nerve function has been linked to increased risk of chronic health conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and depression.
5 Negative Effects of Not Improving Vagus Nerve Function
-
Increased risk of chronic health conditions: Research has shown that poor vagus nerve function is associated with increased risk of chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer. (Source: NCBI)
-
Decreased emotional regulation: The vagus nerve is involved in emotional regulation, and individuals with poor vagus nerve function may experience increased levels of anxiety, depression, and mood instability. (Source: Harvard Health)
-
Higher stress levels: The vagus nerve plays a critical role in the body's stress response, and individuals with poor vagus nerve function may experience higher levels of stress and have a harder time coping with stress. (Source: Psych Central)
-
Impaired digestion: The vagus nerve also plays a role in digestion and individuals with poor vagus nerve function may experience symptoms such as constipation, bloating, and indigestion. (Source: Mayo Clinic)
-
Reduced immune function: The vagus nerve helps regulate the immune system, and individuals with poor vagus nerve function may have a harder time fighting off infections and may be at increased risk for autoimmune disorders. (Source: Frontiers in Immunology)
"It's important to note that while these negative effects have been observed in some studies, not all individuals with poor vagus nerve function will experience them. However, improving vagus nerve function through techniques such as deep breathing, yoga, and cold exposure may help mitigate these potential negative effects."

How To Train The Vagus Nerve
There are various techniques for stimulating the vagus nerve, including deep breathing, yoga, singing, and cold exposure. These techniques have been found to be effective in activating the relaxation response and improving vagus nerve function.
For example, deep breathing exercises involve slow, deep breaths, focusing on exhaling for a longer duration than inhaling. This technique stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and reducing stress levels. Similarly, yoga practices such as asanas, pranayama, and meditation have been found to be effective in activating the vagus nerve and improving overall well-being.
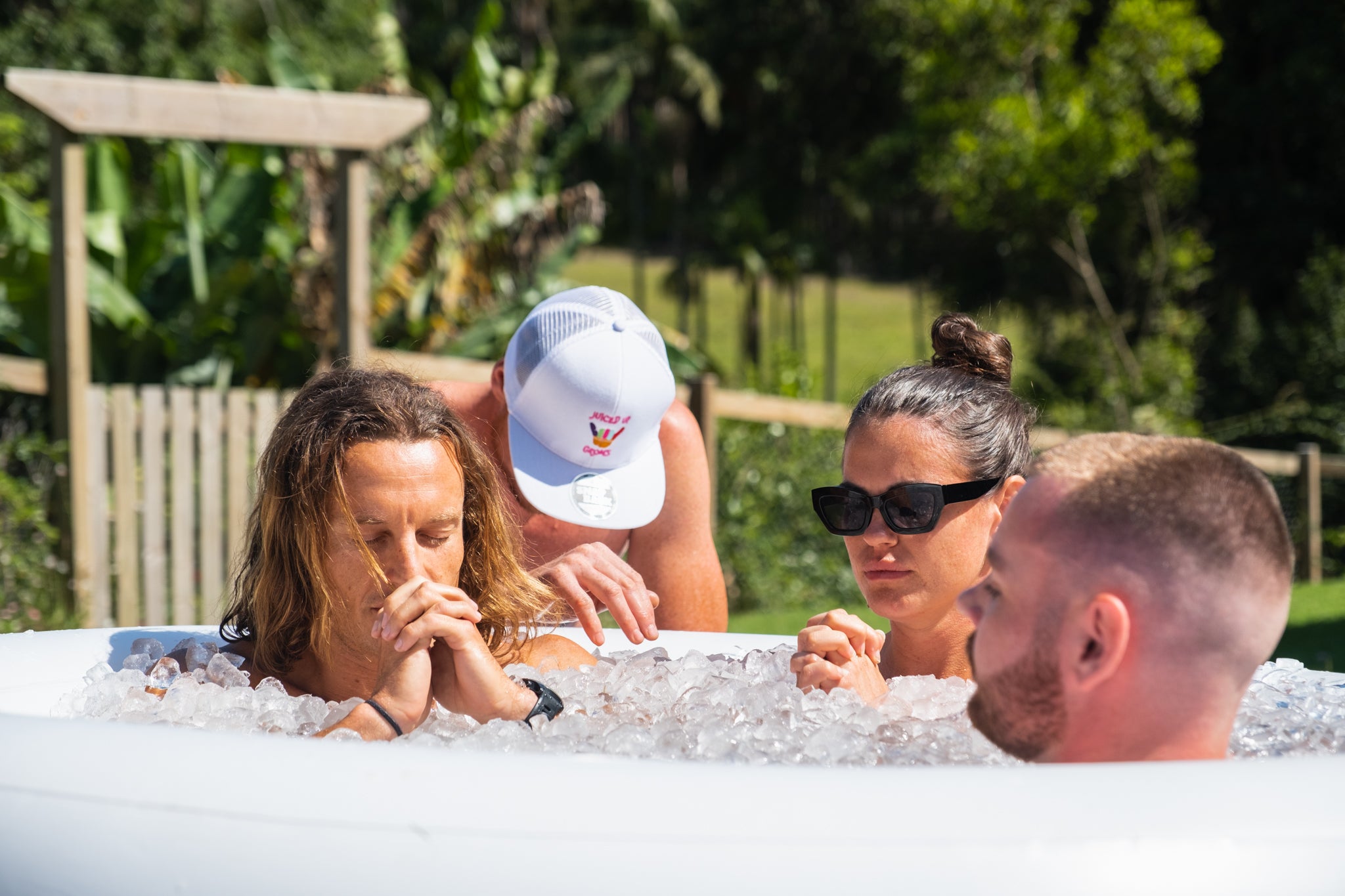
Cold exposure is another technique that has been shown to activate the vagus nerve. Exposure to cold water or ice baths can promote the release of hormones and neurotransmitters that promote relaxation and reduce stress levels.
The Impact of Vagus Nerve Training on Emotional Regulation
The vagus nerve plays a crucial role in emotional regulation, and training it can have significant benefits for our mental health. Studies have shown that vagus nerve stimulation can reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety and improve emotional regulation.
For example, one study found that vagus nerve stimulation can reduce symptoms of depression in patients who have not responded to other treatments. Similarly, another study found that vagus nerve stimulation can improve emotional regulation and reduce symptoms of anxiety in individuals with anxiety disorders.

The Impact of Vagus Nerve Training on Personal and Professional Performance
The vagus nerve also plays a crucial role in personal and professional performance, particularly in high-pressure situations. Training the vagus nerve can help individuals perform better under stress and reduce stress levels during competition.
For example, a study found that vagus nerve stimulation can improve performance outcomes in athletes, particularly in high-pressure situations. Similarly, another study found that vagus nerve stimulation can reduce stress levels and improve performance outcomes in individuals performing tasks under stress.
The Risk of Not Improving Vagus Nerve Function
Chronic stress and anxiety can have negative effects on our physical health, and poor vagus nerve function has been linked to increased risk of chronic health conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and depression. Therefore, it is essential to incorporate vagus nerve training into our daily routine to improve our stress levels, performance, and overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, training your vagus nerve can have a significant impact on your stress levels, emotional regulation, personal and professional performance, and overall health and well-being. By practicing exercises like deep breathing, yoga and cold exposure, you can stimulate the vagus nerve and activate the relaxation response.
On the other hand, not improving vagus nerve function can have negative effects on our physical and mental health, increasing the risk of chronic health conditions. Therefore I'm sure we could all agree that it is essential to incorporate vagus nerve training into your daily routine to improve your stress levels, performance, and overall well-being.
In short think of the vagus nerve as a superhero who can help you fight stress and save the day. Just like how Superman has special powers to protect the city, the vagus nerve has the power to activate your body's natural relaxation response and calm your mind and body. When you train your vagus nerve, you're essentially giving your superhero the tools they need to do their job effectively. Just like how Superman needs his cape and superpowers to save the day, the vagus nerve needs stimulation techniques like deep breathing and cold exposure to activate its powers and help you manage stress. By training your vagus nerve, you become a superhero yourself, with the power to take control of your stress levels and improve your overall well-being.
Want to learn how to breathe to regulate your emotional state?
Click here to learn more: ( How to Use Breathwork to Regulate Your State )

Chris is a Certified Personal Trainer, Strength and Conditioning Coach, Sports Nutrition Advisor, Breathing Performance Coach, Cognitive Behavioural Therapist Coach, Over 10 years experience in the health and fitness industry, while also running his own businesses since 2014 allowing him to implement and practice tools that allowed him to thrive in life.
In the past Chris experienced first hand on how to overcome his own severe anxiety and depression through changing lifestyle habits and behaviours through holistic health.
References:
-
Kox, M., van Eijk, L. T., Zwaag, J., van den Wildenberg, J., Sweep, F. C., & Pickkers, P. (2014). Voluntary activation of the sympathetic nervous system and attenuation of the innate immune response in humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(20), 7379-7384.
-
Steptoe, A., Hamer, M., & Chida, Y. (2007). The effects of acute psychological stress on circulating inflammatory factors in humans: a review and meta-analysis. Brain, behavior, and immunity, 21(7), 901-912.
-
Brown, R. P., & Gerbarg, P. L. (2005). Sudarshan Kriya yogic breathing in the treatment of stress, anxiety, and depression: part I-neurophysiologic model. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 11(1), 189-201.
-
van Diest, I., Verstappen, K., Aubert, A. E., Widjaja, D., Vansteenwegen, D., Vlemincx, E., ... & Van den Bergh, O. (2014). Inhalation/exhalation ratio modulates the effect of slow breathing on heart rate variability and relaxation. Applied psychophysiology and biofeedback, 39(3-4), 171-180.
-
Zaccaro, A., Piarulli, A., Laurino, M., Garbella, E., Menicucci, D., Neri, B., ... & Gemignani, A. (2018). How breath-control can change your life: A systematic review on psycho-physiological correlates of slow breathing. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 12, 353.










Leave a comment